本文讲解回溯算法的原理和具体实现。
1 回溯算法
1.1 回溯算法的原理
回溯算法是暴力搜索法中的一种。回溯法是一种可以找出所有(或一部分)解的一般性算法,尤其适用于约束满足问题。
在实际实现时采用DFS搜索的方式进行遍历,然后再遍历过程中采用剪枝的策略去掉不满足条件的解。
对于具体代码实现而言,实际上就是DFS的一种实际应用。 和DFS遍历二叉树不同之处在于,回溯中使用DFS需要有前进和回退的过程,这也是为啥叫做回溯的原因。
一般在回溯算法中,使用递归的方式来进行DFS。
1.2 解决回溯问题思路
解决回溯问题时,一定要画出遍历路径的多叉树。搞清楚横向遍历的是什么,和纵向遍历的路径是啥?
例如:
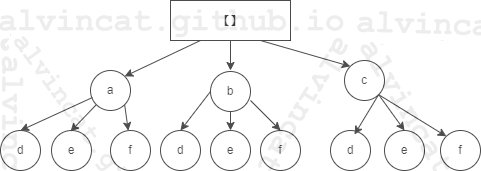
如下图所示,为leetcode 电话号码组合问题中"23"的遍历示意图。其中2对应字符串"abc", 3对应字符串"def"。
我们可以看到,横向展开的是每个字符串内的每个字母,纵向是展开的字符串"23"。
而回溯的递归函数中的for循环内部实现,就是横向展开的体现。
因此在这个问题中,需要先根据索引获取数字对应的字符串。
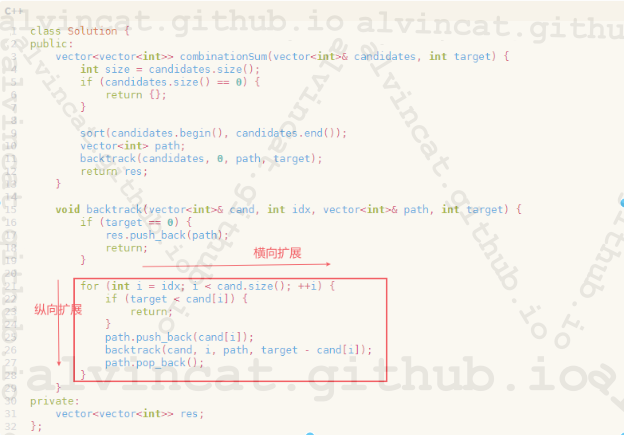
而针对问题39-组合总和问题,可以按照下图所示的思路去分析解决:
1.1.1 回溯代码的基本框架
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
path = []
def backtrack(path, 选择列表):
if 满足结束条件:
result.add(item)
return
for item in 选择列表:
path.push(item) // 添加
backtrack(path, 选择列表)
path.pop() // 删除
|
1.2 回溯算法的应用
1.2.1 排列组合问题
- 问题1: 全排列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
if (len == 0) {
return res;
}
vector<int> path;
vector<bool> used(len, false);
dfs(nums, path, 0, used);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums, vector<int> path, int depth, vector<bool>& used) {
int len = nums.size();
if (len == depth) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if (!used[i]) {
path.push_back(nums[i]);
used[i] = 1;
dfs(nums, path, depth + 1, used);
used[i] = 0;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
};
|
- 问题2:电话号码的字母组合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
int len = digits.size();
if (len == 0) {
return {};
}
string path;
backtrack(digits, 0, path);
return res;
}
void backtrack(string digits, int index, string& path) {
if (index == digits.size()) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
char ch = digits[index];
string str = num_map[ch - '0'];
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); ++i) {
path.push_back(str[i]);
backtrack(digits, index + 1, path);
path.pop_back();
}
}
private:
string num_map[10] = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
vector<string> res;
};
|
- 问题3:组合总和(39)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
int size = candidates.size();
if (candidates.size() == 0) {
return {};
}
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
vector<int> path;
backtrack(candidates, 0, path, target);
return res;
}
void backtrack(vector<int>& cand, int idx, vector<int>& path, int target) {
if (target == 0) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i = idx; i < cand.size(); ++i) {
if (target < cand[i]) {
return;
}
path.push_back(cand[i]);
backtrack(cand, i, path, target - cand[i]);
path.pop_back();
}
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> res;
};
|
1.2.2 N皇后问题
1.3 Leetcode相关题目
-
17 Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
-
22 Generate Parentheses
-
39 Combination Sum
-
46 Permutations
-
51 N-Queens
-
52 N-Queens II
-
77 Combinations
-
78 Subsets
-
89 Gray Code
-
93 Restore IP Addresses
-
111 Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
-
112 Path Sum
-
113 Path Sum II
-
131 Palindrome Partitioning
-
140 Word Break II
![]()
![]()